|
When the lead storage battery is being used as a power source,
oxidation-reduction reactions generate electricity.
When a depleted battery is being recharged, electricity from
an outside source causes oxidation-reduction reactions to
go against the natural free energy gradient.
This same principle of using electric current to bring about
energetically unfavorable chemical changes is used widely
in electrolytic cells.
Many metals can be obtained from their ores (usually oxides
or sulfides) by reducing them with carbon, but the alkali
metals, such as sodium, are too reactive for this.
They must be obtained by electrolysis.
In the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride, the reduction
that cannot be accomplished chemically is carried out electrochemically.
Current is passed through two electrodes immersed in NaCl
heated above its melting point of 8010C.
At one electrode, Cl- ions are oxidized to Cl2
gas, and it therefore is the anode. At the cathode, Na+
ions are reduced to sodium metal.
|
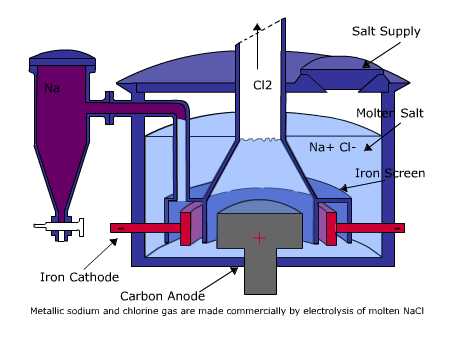
The Cl2 gas is collected and piped away, and
the sodium, which is a liquid at this temperature and lighter
than the fused salt, floats to the surface and is recovered.
|