|
8. Carbon-carbon single bonds in organic and biological molecules
have energies around 83 kcal 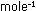 .
From the answers to Problems 5-7, would you expect that red-orange
light is capable of breaking carbon-carbon bonds and disrupting
molecules? .
From the answers to Problems 5-7, would you expect that red-orange
light is capable of breaking carbon-carbon bonds and disrupting
molecules?
9. What is the energy per mole of photons of ultraviolet
light of wavelength 2400 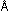 ?
(See Problem 8.) Should this radiation be capable of disrupting
organic molecules? Why are UV lamps used as germicidal sterilizers? ?
(See Problem 8.) Should this radiation be capable of disrupting
organic molecules? Why are UV lamps used as germicidal sterilizers?
10. When light of frequency 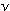 falls on a photocell, an individual electron in the metal surface
is given an energy kick of E = h
falls on a photocell, an individual electron in the metal surface
is given an energy kick of E = h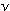 .
The kinetic energy that the ejected electrons will have is given
by KE = h .
The kinetic energy that the ejected electrons will have is given
by KE = h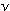 -
- 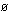 ,
in which ,
in which 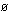 is called the "work function" of the metal, and is the energy needed
to pull an electron out of the metal surface. The work function
is similar to the first ionization energy, but applies to the removal
of an electron from a block of metal instead of from an isolated
gaseous atom. The incoming photons of light must have energy at
least as large as
is called the "work function" of the metal, and is the energy needed
to pull an electron out of the metal surface. The work function
is similar to the first ionization energy, but applies to the removal
of an electron from a block of metal instead of from an isolated
gaseous atom. The incoming photons of light must have energy at
least as large as 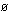 ,
or they cannot remove electrons at all. Does this mean that there
is a maximum wavelength, or a minimum wavelenlgth, for photoemission
of electrons from a metal surface? ,
or they cannot remove electrons at all. Does this mean that there
is a maximum wavelength, or a minimum wavelenlgth, for photoemission
of electrons from a metal surface?
|
|