|
1. The
equilibrium constant for the reaction
 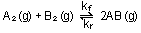
at a given temperature is 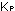 = 2.5 X 10
= 2.5 X 10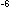 .
The quantities .
The quantities 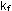 and
and 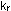 are the
forward and reverse rate constants. If the reverse rate constant
has a numerical value of 151 atm are the
forward and reverse rate constants. If the reverse rate constant
has a numerical value of 151 atm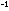 sec
sec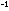 ,
what is the value of ,
what is the value of 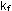 ? ?
2. The equilibrium constant for the reaction
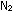 + + 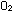
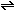 2NO at
2130 2NO at
2130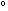 C is
2.5 x 10 C is
2.5 x 10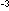 .
What are the units for this equilibrium constant? What is the numerical
value for the equilibrium constant for the reaction NO .
What are the units for this equilibrium constant? What is the numerical
value for the equilibrium constant for the reaction NO 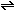 1/2
1/2 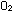 + 1/2 + 1/2
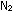 ? ?
3. Does the synthesis of NO as described in Problem 2 occur
with the absorption, or emission, of heat? For the following conditions,
decide whether the gas mixture described is at equilibrium, or whether
a net forward or reverse reaction will take place spontaneously:
(a) A 1-liter box contains 0.020 mole of NO, 0.010 mole of 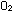 ,
and 0.020 mole of ,
and 0.020 mole of 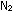 at 2130
at 2130 C. C.
(b) A 20-liter box contains 1 x 10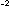 mole of
mole of 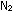 ,
1 x10 ,
1 x10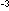 mole of
mole of 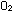 ,
and 2 x 10 ,
and 2 x 10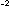 mole of NO at 2130
mole of NO at 2130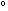 C. C.
|
|
(c) A 1-liter box contains
1.00 mole of 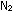 ,
16 moles of ,
16 moles of 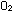 ,
and 0.2 mole of NO at 2500 ,
and 0.2 mole of NO at 2500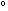 C. C.
4. At 25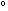 C
and 20 atm pressure, the reaction C
and 20 atm pressure, the reaction
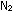 (g) + (g) +
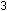 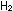 (g)
(g) 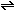 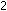 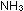 (g) has a standard enthalpy change of -22.1 kcal per mole of
(g) has a standard enthalpy change of -22.1 kcal per mole of 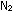 . .
(a) If the temperature is raised to 300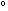 C
while the pressure is held at 20 atm, will more ammonia be present
at equilibrium, or less? C
while the pressure is held at 20 atm, will more ammonia be present
at equilibrium, or less?
(b) If the pressure is increased to 30 atm while the temperature
remains at 25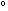 C,
will more, or less, ammonia be present, compared with initial conditions? C,
will more, or less, ammonia be present, compared with initial conditions?
(c) If half the ammonia is removed and the system is allowed to
come to equilibrium again, will the amount of nitrogen gas present
increase, or decrease?
(d) What will be the effect on the original equilibrium mixture
if a catalyst for ammonia synthesis is added?
|