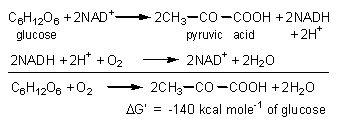|
The successive drops in free energy that occur during these reactions
are shown right. The overall reaction is So carbon dioxide and water are plotted 686 kcal below the level of glucose. The process of glycolysis, or conversion of glucose to two pyruvate molecules, only leads to a 140 kcal fall in free energy:
The process is anaerobic only if the NADH produced is reused to convert pyruvate to lactate or ethanol. Otherwise, 02 is required to reoxidize NADH to NAD+. Glycolysis requires ten successive reactions, each controlled by its own enzyme. It is one of the oldest series of reactions in living organisms and is common to all forms of life. |
The series of reactions yields two molecules of ATP per glucose molecule, and two molecules of NADH, which eventually produce 6 more ATP, or 8 ATP in all. Of the 140 kcal of free energy released per mole of glucose, 8 X 7.3 = 58.4 kcal are saved via ATP, again a 42% energy conversion. |
|