|
Carbon monoxide, like the isoelectronic 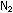 molecule, is barely soluble in water. Carbon dioxide dissolves easily
in water to form carbonic acid:
molecule, is barely soluble in water. Carbon dioxide dissolves easily
in water to form carbonic acid:
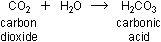
This is a weak acid with a sharp taste, familiar from carbonated
soft drinks. The bubbles in a carbonated drink are incompletely
dissolved 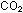 gas.
gas.
When 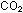 dissolves in water, the carbon atom attracts a lone pair from the
oxygen of a water molecule and forms carbonic acid, which has the
structure shown on the next page. The carbon atom is double-bonded
to one oxygen atom, and single-bonded to each of two OH groups.
dissolves in water, the carbon atom attracts a lone pair from the
oxygen of a water molecule and forms carbonic acid, which has the
structure shown on the next page. The carbon atom is double-bonded
to one oxygen atom, and single-bonded to each of two OH groups.
Since carbon is moderately electronegative and the C-O bond in C-O-H
is stronger than the O-H bond, the carbonic acid molecule dissociates
in water by losing protons, and therefore is an acid. Dissociation
takes place in two steps:
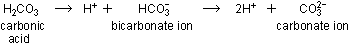
|
|
|