|
Every
chemical process is reversible on the molecular level. If A molecules
can change into B molecules, then B must be able to change into
A, although perhaps at a different rate. If 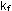 and
and 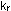 are the
rate constants for the forward and reverse reactions, then as in
the crabapple analogy, are the
rate constants for the forward and reverse reactions, then as in
the crabapple analogy,
forward rate = forward rate constant x concentration of reactants
  =
= 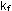 [A] [A]
reverse rate = reverse rate constant x concentration of products
  =
= 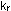 [B] [B]
[A] and [B] are the concentrations of molecules of A and B. Instead
of units of apples per square foot, we measure molecular concentrations
in molecules per cubic centimeter, or more conveniently, moles of
molecules per liter (1 mole = 6.022 X 10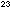 molecules and 1 liter = 1000 cm
molecules and 1 liter = 1000 cm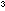 ).
If overall reaction rates are expressed in moles of substance reacting
per second, then the rate constants, ).
If overall reaction rates are expressed in moles of substance reacting
per second, then the rate constants, 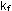 and
and 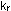 have units
of liters per second: have units
of liters per second:
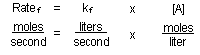
These rate constants again describe how fast each of the forward
and reverse reactions "cover the territory" that the molecules occupy.
|
|