Table of some oxy-acid salts containing chlorine
|
Oxidation
State
|
Formula
|
Name
|
Structure
|
Remarks
|
|
+1
|
ClO-
|
Hypochlorite
(monooxochlorate)
|
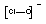
|
Good oxidising agent.
|
|
+3
|
ClO2-
|
Chlorite
(dioxoxchlorate)
|
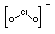
|
Strong oxidising agent
disproportionates.
|
|
+5
|
ClO3-
|
Chlorate
(trioxochlorate)
|
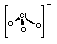
|
Oxidising agent.
|
|
+7
|
ClO4-
|
Perchlorate
(tetraoxochlorate)
|
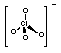
|
Oxidising agent and
weak acid.
|
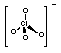
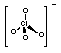
 2H+ + 2OH- DGo>0
2H+ + 2OH- DGo>0 X- + XO- + H2O DGo<0,
favourable for all X.
X- + XO- + H2O DGo<0,
favourable for all X.