Interhalogens
Neutral Interhalogens
|
XY
|
XY3
|
XY5
|
XY7
|
|
IF
|
IF3
|
IF5
|
-
|
|
BrF
|
BrF3
|
BrF5
|
-
|
|
ClF
|
ClF3
|
ClF5
|
-
|
|
ICl
|
(ICl3)2
|
-
|
-
|
|
BrCl
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
IBr
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Polyhalogen cations
|
X2+
|
XY2+
|
X2Y+
|
XYZ+
|
XY4+
|
XY6+
|
|
Br2+
|
ClF2+
|
Cl2F+
|
BrICl+
|
ClF4+
|
ClF6+
|
|
I2+
|
BrF2+
|
I2Cl+
|
-
|
BrF4+
|
BrF6+
|
|
-
|
IF2+
|
I2Br+
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
-
|
IBr2+
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Polyhalogen anions
|
Xn-
|
XYn-
|
XYZn-
|
XnY-
|
XYnZ-
|
|
I3-
|
IF6-
|
IBrCl3-
|
I2Br-
|
ICl3F-
|
|
-
|
IF8-
|
IBrCl-
|
I2Cl-
|
-
|
|
-
|
ICl4-
|
IBrF-
|
-
|
-
|
|
-
|
BrF6-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
-
|
IF4-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
-
|
ClF4-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
-
|
BrCl2-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
Structures
All thermally stable, so reflects extensive chemistry.
High positive oxidation state examples:
ClF5, BrF5, IF7,
Low oxidation state examples:
BrF, IF disproportionate
BrCl, IBr, ICl, stable
(ICl2)2 only +3 oxidation state
stable with chlorine.
Synthesis:
direct combination works well.
Properties:
diamagnetic, sensitive to hydrolysis.
ClF5 + H2O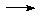 ClO2F
+ HF
Good halogenating agents:
most E-X bonds stronger
ClF3 made on large scale for the nuclear industry.
U2Oy
ClO2F
+ HF
Good halogenating agents:
most E-X bonds stronger
ClF3 made on large scale for the nuclear industry.
U2Oy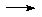 UF6
Cations and anions
nearly all combinations known.
halide donor anions.
MX + EXn
UF6
Cations and anions
nearly all combinations known.
halide donor anions.
MX + EXn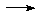 M+[EX(n+1)]-
Route to mixed interhalogen ions.
need large cation since B(E-X) can then compensate
for drop in lattic energy.
M+[EX(n+1)]-
Route to mixed interhalogen ions.
need large cation since B(E-X) can then compensate
for drop in lattic energy.
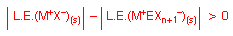 Cations EXn+
Good halide acceptor are: AsF5, SbF5,
SbCl5, AlCl3
Need strong A-X bonds + high lattice energy.
Since no BrF7
Cations EXn+
Good halide acceptor are: AsF5, SbF5,
SbCl5, AlCl3
Need strong A-X bonds + high lattice energy.
Since no BrF7 BrF5
+ KrF2 + AsF5
BrF5
+ KrF2 + AsF5 BrF6+
cf NF4+
Due to small size of F- can get high coordination
numbers.
VSEPR rules work for predicting structures.
Note I2Cl6, dimer but contrasts
with AlCl3.
BrF6+
cf NF4+
Due to small size of F- can get high coordination
numbers.
VSEPR rules work for predicting structures.
Note I2Cl6, dimer but contrasts
with AlCl3.