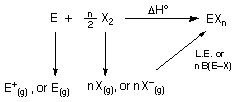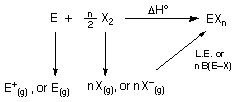Halides
Born-Haber cycle for
the synthesis of a halide compound:
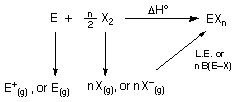 In general, fluorine stabilises high oxidation
state compounds.
Explaination of trends:
1. Weak F-F bond (also kinetic argument).
2. Strong B(E-F) bonds, (F > Cl > Br > I).
3. High electron affinity, cf. DHf[X-(g)].
4. High lattic energy, small F-
ion (F>Cl>Br>I), Kapustinskii approximation.
Low to intermediate oxidation states. EF2
unstable with respect to disproportionation (eg. SF2).
Covalency increases with oxidation state.
Covalency increases down the series F
In general, fluorine stabilises high oxidation
state compounds.
Explaination of trends:
1. Weak F-F bond (also kinetic argument).
2. Strong B(E-F) bonds, (F > Cl > Br > I).
3. High electron affinity, cf. DHf[X-(g)].
4. High lattic energy, small F-
ion (F>Cl>Br>I), Kapustinskii approximation.
Low to intermediate oxidation states. EF2
unstable with respect to disproportionation (eg. SF2).
Covalency increases with oxidation state.
Covalency increases down the series F  I.
Lower oxidation state tends to be formed with
Br and I.
High oxidation state fluorides tend to be molecular.
I.
Lower oxidation state tends to be formed with
Br and I.
High oxidation state fluorides tend to be molecular.