Hydrogen bonding is the interaction between a H-atom bound to an electronegative atom and another atom that is generally also electronegative and has one or more lone pairs. This can be represented as:
![]()
- X-H is a proton donor, and Y an acceptor.
- Strongest when both X and Y are first-row elements, especially if X and/or Y = N, O, F
- Other groups, with X = P, S, Cl, Br, can also be proton donors. Even C-H bonds can be proton donors if the carbon is attached to electronegative groups, e.g., CHCl3.
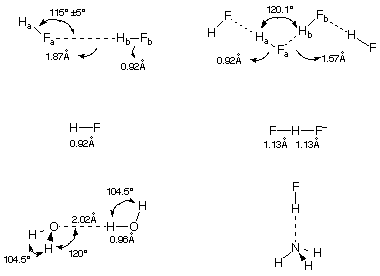
Figure 2: Examples of hydrogen bonded molecules and ions