Boron Halides (BbXx)
Synthesis of BF3
Na2B4O7 +
6CaF2 + 8H2SO4 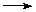 2NaHSO4 + 6CaSO4 + 7H2O + 4BF3
Essentially
B4O72- + "HF"
2NaHSO4 + 6CaSO4 + 7H2O + 4BF3
Essentially
B4O72- + "HF" 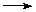 "BF3" + "H2O"
Compare:
NaCl + H2SO4
"BF3" + "H2O"
Compare:
NaCl + H2SO4 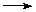 NaHSO4
+ HCl
Synthesis of BCl3
B2O3 + 3Cl2
+ 3C
NaHSO4
+ HCl
Synthesis of BCl3
B2O3 + 3Cl2
+ 3C 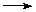 2BCl3 + 3CO (dry conditions)
Synthesis of BI3
NaBH4 + 2I2
2BCl3 + 3CO (dry conditions)
Synthesis of BI3
NaBH4 + 2I2  BI3 + NaI + 2H2
Properties of B(Hal)3
Compounds
All planar, monomeric, strong Lewis acids (many complexes)
Order of Lewis acid strength
BF3 < BCl3 < BBr3
< BI3
Against electronegativity trend (F should induce
strongest d+ charge on boron atom)
Ans: p-bonding
BI3 + NaI + 2H2
Properties of B(Hal)3
Compounds
All planar, monomeric, strong Lewis acids (many complexes)
Order of Lewis acid strength
BF3 < BCl3 < BBr3
< BI3
Against electronegativity trend (F should induce
strongest d+ charge on boron atom)
Ans: p-bonding
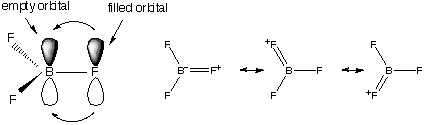 Compare with Al: Al2Cl6 =>
weak intramolecular p-bonding dimer
BCl3 => strong intramolecular p-bonding
monomer
Reaction with Water
BX3 + 3H2O
Compare with Al: Al2Cl6 =>
weak intramolecular p-bonding dimer
BCl3 => strong intramolecular p-bonding
monomer
Reaction with Water
BX3 + 3H2O  H3BO3 + 3HX X = Cl, Br, I
whereas
H3BO3 + 3HX X = Cl, Br, I
whereas 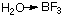
 H3O+[BF3(OH)]-
H3O+[BF3(OH)]-  BF3(g)
Due to very strong B-F bond
Lower Halides
B2X4, B4X4,
B8X8, B9X9
all have B-B bonds
BF3(g)
Due to very strong B-F bond
Lower Halides
B2X4, B4X4,
B8X8, B9X9
all have B-B bonds

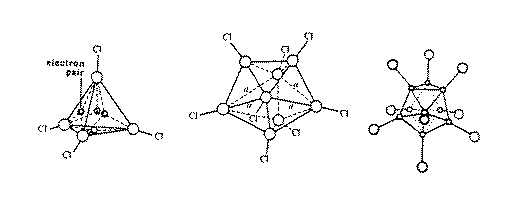 Figure 9:
The lower boron halides-B4Cl4 has a perfect tetrahedral
structure,
the larger Bn units have long and short B-B distances
Figure 9:
The lower boron halides-B4Cl4 has a perfect tetrahedral
structure,
the larger Bn units have long and short B-B distances
 2NaHSO4 + 6CaSO4 + 7H2O + 4BF3
2NaHSO4 + 6CaSO4 + 7H2O + 4BF3 2NaHSO4 + 6CaSO4 + 7H2O + 4BF3
2NaHSO4 + 6CaSO4 + 7H2O + 4BF3 "BF3" + "H2O"
"BF3" + "H2O" NaHSO4
+ HCl
NaHSO4
+ HCl 2BCl3 + 3CO (dry conditions)
2BCl3 + 3CO (dry conditions) BI3 + NaI + 2H2
BI3 + NaI + 2H2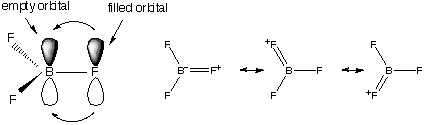
 H3BO3 + 3HX X = Cl, Br, I
H3BO3 + 3HX X = Cl, Br, I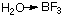
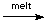 H3O+[BF3(OH)]-
H3O+[BF3(OH)]- 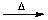 BF3(g)
BF3(g)
