|
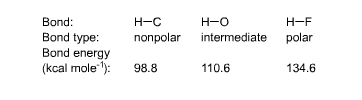
We can pull everything in this chapter together and bring it to a close by taking a second look at a question that was raised in Chapter 6 and again at the beginning of this chapter: Why is fire hot? The answer given previously was that oxidations give off heat because electrons in the product molecules are shifted toward the electronegative O or F atoms, and the molecules are more stable as a result. Now, with the aid of bond energies, we can stop being qualitative and put numbers to our argument. The bond-energy values in the table
on Page 22 support the assertion that the more the electrons in
a bond are shifted toward an electronegative atom, the more stable
the bond is. Single-bond energies between H and some other elements
are |