|
For a general reaction, in which a moles of substance A and
b moles of B react to form c moles of C and d
moles of D,
 a A + b B
a A + b B 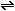 c C + d D
c C + d D
the equilibrium-constant expression is
 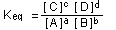
This is the law of mass action.
Concentrations can be measured in any terms that express the relative
numbers of molecules per unit volume. In solutions, concentrations
usually are given in molarity, or moles per liter, 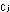 .
This is indicated by a subscript C to the equilibrium constant: .
This is indicated by a subscript C to the equilibrium constant:
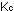 .
Gases sometimes are measured in moles per liter also, but more often
are measured in mole fractions, .
Gases sometimes are measured in moles per liter also, but more often
are measured in mole fractions, 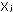 ,
or in partial pressures, ,
or in partial pressures, 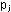 .
(The subscript j simply refers to any species.) The equilibrium
constants using these units are indicated by .
(The subscript j simply refers to any species.) The equilibrium
constants using these units are indicated by 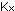 and
and 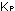 . .
|
|
The mole fraction of the
jth component of a gas mixture, 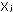 ,
is the number of moles of that particular gas, divided by the total
number of moles of all gases present: ,
is the number of moles of that particular gas, divided by the total
number of moles of all gases present:
 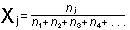
Our atmosphere has one molecule of 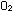 for every four molecules of
for every four molecules of 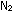 ; thus the mole fraction of oxygen gas is
; thus the mole fraction of oxygen gas is
 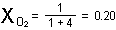
and that of nitrogen is
 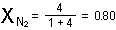
The sum of mole fractions of all the gases in a mixture, of course,
must be exactly one.
|