|
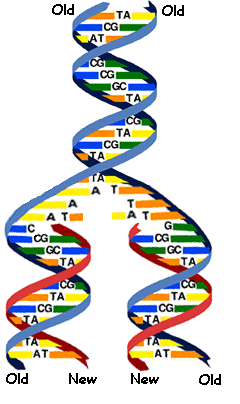
This base pairing provides a means of duplicating the DNA during cell division. Each strand of the parent DNA molecule unwinds, and different nucleoside triphosphates (deoxyadenosine triphosphate, dATP; deoxycytidine triphosphate, dCTP; etc.) are paired with the exposed bases on each strand. The free energy of the triphosphate is used to connect these paired nucleotides into a 5`-3` polymer, so that each of the parent DNA strands now is paired with a new strand identical to the one from which it separated. This replication process is shown schematically on the right. The result is two daughter helices, each identical with the parent in base sequence and pairing, and each containing one of the parent strands and one newly polymerized strand. The double helix is not only a protection, it is the basis for reproduction. Right: DNA is replicated by unwinding the two strands and building a new complementary strand to each. The daughter molecules are exact copies of the parent, each with one of the parent strands. Based and adapted from James D. Watson, Molecular Biology of the Gene, Second Edition, W. A. Benjamin, Inc. Copyright © 1970 J. D. Watson. |
|